- There are 3 different types of circuits . their is a series circuit , a parallel circuit and their is compound circuits .
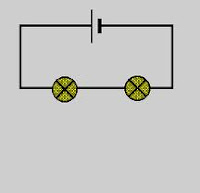
in a series circuit the users or the components are in a series to each other for example :
also if their is a 12 voltr battery supply it is shared between the two components in the circuit .
so if you made a two bulb series circuit the bulbs would be using about 6volts each and the amperage stays the same but the resistance is increased . In class we made this circuit by using some wires and a circuit bord with a switch light bulbs and a fuse and i linked all these components together in series . and we ran some tests using a multimeter and i checked the voltage drop by runing the multimeter across the components to check for bad switches or faulty connections .
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
In a parallel circuit you have a battery input and a out put which goes to ground .
a parallel circuit is when all the users or components eg. light bulbs are in parallel row form here is an example of a 3 bulb parallel circuit . The voltage is aproxamitly the same throughout the bulbs because unlike a series circuit the available voltage dosen't change because all the lights have their own power supply and there own ground . 

COMPOUND CIRCUIT
a compound circuit is when there are light bulbs or components in parallel and series to each other
so if you made a compound circuit for example you would have two bulbs in parallel and one bulb in a series and it would look something like this :
i learn't that when working out calculations of the resistance of a compound circuit always work the total of the parallel circuit first .and they all get round about the same volts because there only one light in series and the two in parallel have there own battery supply so the 1 series light bulb gets the same because there is nothing taking power from it . we also checked the v.d over the circuit the series had the biggest drop because it use all its power .